Definition of SKUd
SKUd is a DDM Terminology and it’s a portmanteau which is consisted of “SKU” and “d”.
SKU – A Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) is a unique alphanumeric code used by businesses to identify and track their inventory. SKUs are often represented as barcodes or QR codes and are essential for managing stock levels, sales, and product details.
Although we (DDM) is selling service instead of physical goods, the term SKU is still suitable to use in our company because we need to keep track of how many time of the service we had sold out.
d – To differentiate the service between DDM and client’s of DDM, a suffix “d” is added at the end of the Term SKU only in DDM’s SKU.
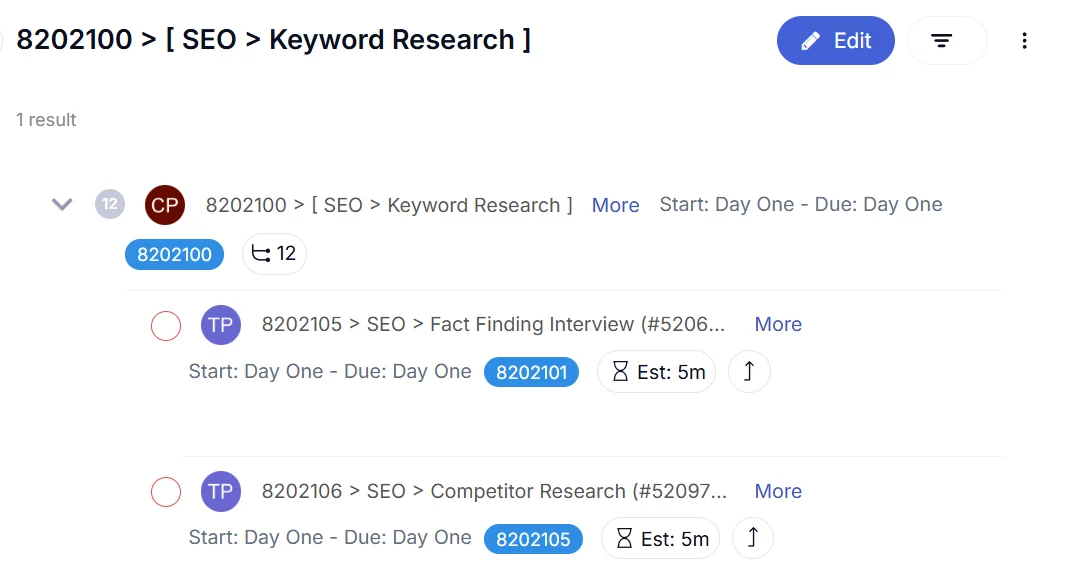
Example of SKUd
#8202100
What Problems Do SKUd Solve
Ambiguous Scope of Service
The big difference between a business which is selling Physical Product and Service is that while the deliverable of a Physical Product is well defined, the deliverable of Service is always ambiguous and Goalpost shifting.
For example, in a website development service, creating 100 Pages involved the cost much higher than creating 10 pages. But most of the time the quotation does not clearly quantity the deliverable in terms of Pages.
Even worse, the definition of a “Page” is hard to define because while some pages are generated dynamically by fetching the data from the database, some pages are created statically .
The wording “Creating a Page” has an ambiguous meaning which does not define whether the content of the Page is fetched from the database or is manually installed.
While different ways of production will involve different amounts of cost and labour hours, dispute will be derived during the project.
To define an quantifiable SKUd is to avoid these disputes.
What you Sold is not What you Produce
While the ultimate goal of a Salesperson is to earn the commission by selling out the service, the objective of a production team is to produce and deliver the service.
While the more details a Salesperson describes the service to the client, the harder the service can be sold out. On the contrary, the more details a Project Manager defines for the service, the easier he/she can deliver the service.
You can see that in most cases the Salesperson and the Project Manager are in conflicts of interest.
For example, due to the incompetent of the knowledge of website development, the Salesperson may not realise that a SMTP Service is a prerequisite for creating a Contact Us Form and therefore exclude the SMTP function from the sales contract.
When the Project Manager takes over the project and realises that while one of the deliverables is a Contact Us Form but the sales contract does not charge the SMTP function, the extra workload which is not absorbed by the sales contract revenue will be involved, and hence the company will lose the money.
A SKUd is here to clearly define and quantify the scope of service which is saleable and executable.
Knowledge it not monetized
Do you still remember the linear algebra equation learnt in your secondary school life ? Or do you still remember how Napoleon took power in France?
While we had spent thousands of hours in our school life learning, we all experienced that most of the knowledge we learnt are forgotten as we seldom have any chance to get use of the knowledge.
If the money spent on study is an “Investment” , then the “Return” on “Investment” is very little for our school life.
The same problem happened in the journey of studying digital marketing. If we do not turn the knowledge to become the service item shown in the quotation, what we have learnt cannot be monetized. (We called it Knowledge Monetization).
To monetize the knowledge, we have to do the mapping among Problem Patterns and Solutions aroused during our study, as well as the Deliverables that we are going to deliver to our client.
For example, during the self-study online you realise the Problem Pattern that WordPress does not have any built-in function to send out the administrative email automatically. And after another 4 hours of studying online you realise that to make WordPress ready to send administrative email, the Solution is that you have to install an SMTP plugin , as well as subscribe for a SMTP Service from the Web Hosting company.
And therefore you go for the SKUd Library and found out that SKUd #83102 is the service which clearly defines the deliverable of installing SMTP Plugin in WordPress, as well as the SMTP yearly subscription plan. The SKUd is here to act as a quantifiable and measurement Deliverables which links up the Problem Patterns and Solutions.
Components of SKUd
#
The “#” is simply denoted as “Number”
1ST DIGIT
8 – Represent the SKUd which is open for sale
5 – Represent the SKUd which is for internal use only. (i.e. not for sale)
2ND – 5TH DIGITs
The 2nd to 5th digit of in the SKUd# is simply an unique number to represent each SKUd.
6TH – 7TH DIGITs
The 6th – 7th (i.e. Last two) Digit represent the Sub Task of an Task Instruction. Due to the fact that 1 SKUd# will have many Tasks in order to delivery the service, the 6th – 8th Digits are assigned to index each Sub Task of the SKUd.
Due to the fact that our service is charged on Sub Task basis, you can expect that sub SKUd for Sub Task can be sold separately, or sold as an “Top Up Item” of a SKUd.
Example of SKUd for Sub Task
- #8202101
- #8202102
- #8202103
Relationship between SKUd and other Business Objects in DDM
- One
QuotationHAS_MANYQuotation Item - ONE
Quotation ItemHAS_ONESKUd (1-7 digit) - One
SKUd (1-5 digit)HAS_ONEDDM Eshop Product Page - ONE
SKUd (1-5 digit)HAS_ONETeamwork Task List - ONE
Teamwork Task ListHAS_MANYSKUd (1-7 digit) - ONE
SKUd (1-7 digit)HAS_ONETeamwork Task/Sub Task
SKUd is acting as the centrality among Sales Team (in terms of Quotation and DDM Eshop Product Listing) , Production Team (in terms of Teamwork Task) and Business Development Team (In Terms of bGraph) , so that all 3 departments can be co-operate cohesively
<<W.I.P>>Relationship among SKUd , Selling and Production
- Problem Pattern – Producer will do more task then it is suggested, which will duplicated to the task scope of another SKUd.


Leave a Reply