Category: Knowledge Base
-
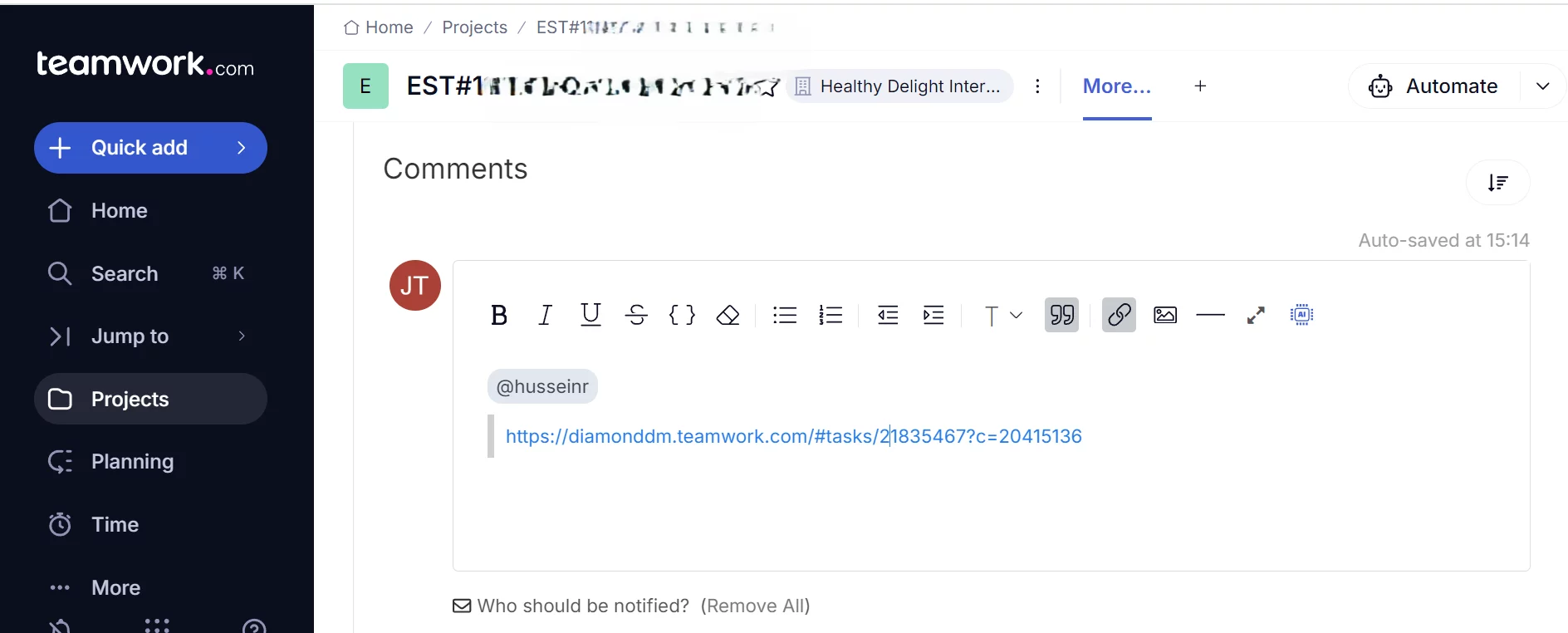
How to Comment in Teamwork.com
Definition Comment in Teamwork.com can be used to response any Task , SubTask or Milestone by either assignee (i.e. collaborator) or the assignor (i.e. Project Manager) of the Task. How Comment in Teamwork.com looks like What Problem Patterns the Comment solved Accessability Not only can you use the Teamwork.com interface to place the comment, but…
-
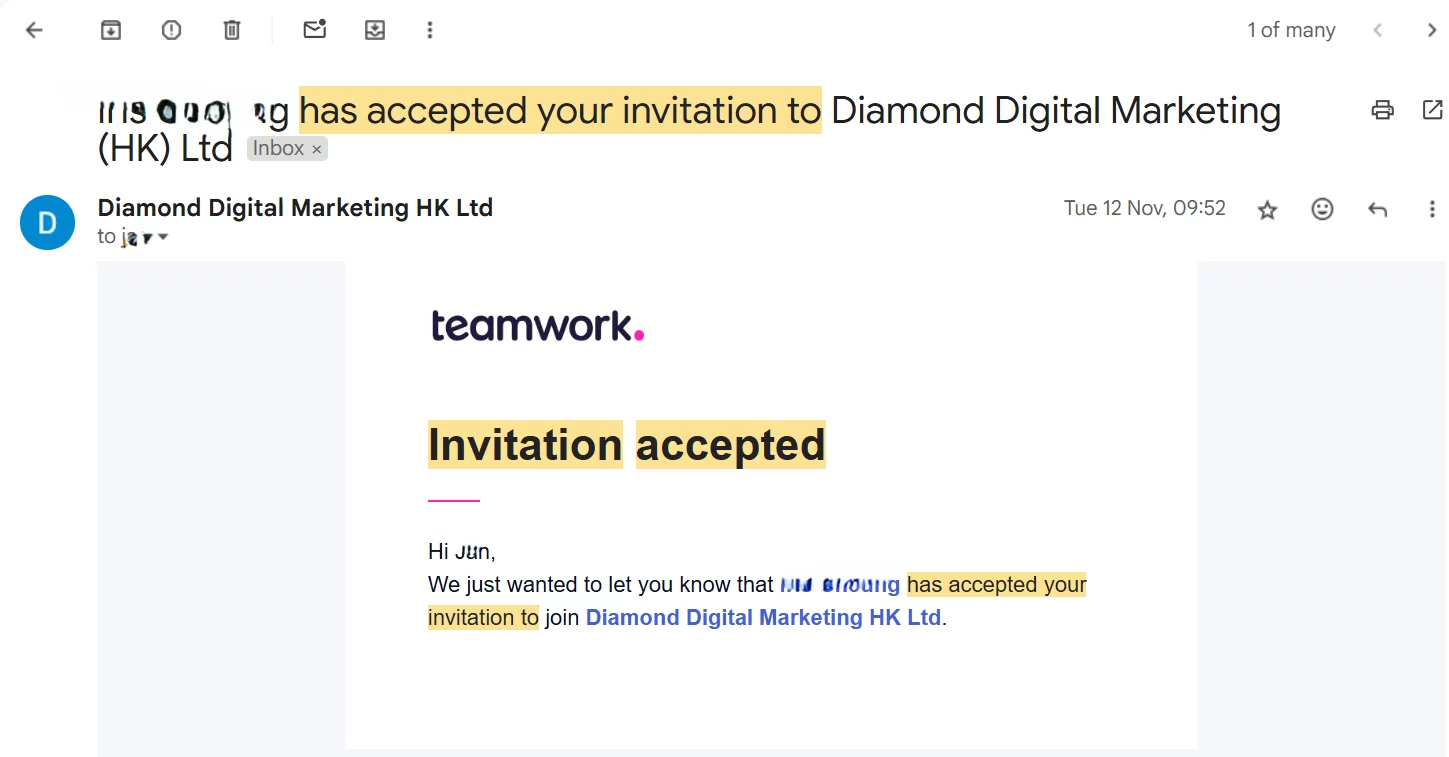
Inviting Collaborator to Join Project Management System
Definition Project Management System In DDM Group, we will adapt teamwork.com as the Project Management System, which is used by tens of thousands of orangisation in the world. Whom to Invite Administrator Supervisors or Project Managers in DDM Group will be invited as Administrator. Standard User Any non Administrator teammates but own an domain email…
-
Access Rights – DDM Github Profile
Definition Github GitHub is a web based platform that provides hosting for software development and version control using Git. It’s widely used for code collaboration, allowing developers to work together on projects, track changes, and manage different versions of their code. GitHub also offers features like project management, code review, and issue tracking, making it…
-

Assign Google Analytics 4 Access Rights to Others
About Google Analytics 4 (GA4) Google Analytics 4 (“GA4”) is a tracking and measurement tools provided by Google freely to the public. In this article, we will mainly focus on how to assign access rights to others who manage the GA4 on behalf of you. When to assign Access Rights to others Keep secret to…
-
What is a Pivot Table
Introduction Pivot Table is a feature which you can usually see in the Google Spreadsheet and Microsoft Excel. While alots of people can address it existence, seldom people can explain what it is and what it’s difference between the normal table. In this article, we are going to break it down and elaborate it in…
-
Bingo! Theory
Introduction When you search in the internet, although there is many other theory with the same name , Bingo! Theory (remarks : the “!” does matter) is a terminology which is invented by Diamond Digital Marketing to explain the priority of a project go vertically or horizontally. What is Bingo in real life Bingo is…

